In the middle of difficulty lies opportunity.” — Albert Einstein
In the early 80s organisations followed strict top-down rules. Managers gave orders; employees followed. Conflict was something to hide. Team-based structures grew later, bringing more collaboration and more disagreements. Today, workplaces are diverse, digital, fast-paced, and global. Conflict is natural and expected.
The real question isn’t how to avoid conflict, but how to handle it wisely.
As a trainer, I believe that the biggest opportunity is helping teams move from avoiding conflict to facing it with ownership.
Types of Conflict?
Task-Based Conflict:
Disagreements about goals, methods, or timelines.
Relationship Conflict:
Stems from personal differences, miscommunication, or personality clashes.
Process Conflict:
Occurs when people disagree on procedures or how work should be done.
Value-Based Conflict:
Arises from deeply held beliefs or ethics.
What Causes Conflict? (Components of Conflict)
Conflict usually begins when people see things differently. It can come from:
1. Different perceptions and goals
People may disagree about what the real problem is or how to solve it.
2. Poor communication
Lack of open communication often leads to misunderstandings and frustration.
3. Competition for limited resources
Time, money, recognition, tools, or even workspace, when resources are limited, conflict becomes natural.
4. Inconsistency in rules or policies
When rules are unclear or not applied fairly, people feel confused or treated unfairly.
5. Diversity in values, styles, and backgrounds
Different generations, cultures, thinking styles, and personal values can create differences.
6. Interdependency in teams
When people depend on each other to finish tasks, delays or different priorities can easily cause conflict.
7. Emotional Intelligence (EQ)
People with higher EQ communicate better, show empathy, and manage their emotions well. This helps avoid unnecessary conflict.
SIGNS OF CONFLICT:
- Decreased Communication: If employees stop speaking to each other.
- Body Language Cues: Tense posture, lack of eye contact, or closed-off body language
- Behavioral Changes: More withdrawn, defensive or combative.
- Gossip and Complaints: Increased informal complaints, or side conversations about colleagues.
- Changes in Performance: A noticeable drop in an employee’s performance.
IMPACT OF UNRESOLVED CONFLICT:
- Productivity drops because employees lose focus when conflict remains unresolved.
- Morale declines, leading to disengagement, burnout, and low motivation.
- Turnover increases as employees may leave to escape ongoing conflict.
- Teams become fragmented, harming collaboration and unity.
- Unresolved issues can escalate into legal or financial problems for the organization.
Five Ways People Usually Handle Conflict
According to conflict-resolution models:
- Ignore – Avoid the conflict completely.
- Win–Lose – One person pushes to “win” the argument.
- Lose–Win – One person gives in for peace.
- Lose–Lose – Both sides compromise but neither gets what they truly want.
- Win–Win – Both sides work together to find a solution that benefits everyone. (Best method as it creates trust, clarity, and real teamwork.)
Case Study 1: The Three-Generations (Ref 1)
A mid-sized tech company had employees from three generations — Millennials, Gen X, and Baby Boomers. The conflict started because:
- Boomers preferred formal meetings
- Millennials preferred quick chat updates
- Tasks started falling behind, frustrations increased, and people left the company

What HR Did:
- Mapped communication styles and expectations
- Held open sessions for team members to share challenges
- Created a clear working charter
- Used a “collaboration first” approach (Harvard Business School Online)
- Reverse Mentoring: Young employees taught senior leaders about tech trends
- Quarterly “Check-Ins”: Replaced yearly reviews for constant feedback
- AI-based Learning Platform “iON”: Personalized micro-learning and certifications
Result:
- Productivity increased by 18%
- Voluntary resignations reduced by 40%
- 82% improvement in digital adoption among older generations
- 21% drop in Gen Z attrition within 18 month
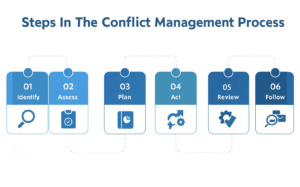
Conflict Resolution Strategies:
Step 1: Acknowledge the Issue
Step 2: Listen Actively to all stakeholders
Step 3: Identify the Root Causee
Step 4: Brainstorm Possible Solutions
Step 5: Discuss benefits and ownership of potential solution
Step 6: Work on a Solution
Early Intervention Matters:
CIPD reminds us: “Workplace conflict can seriously undermine performance and productivity.”
Talk openly, conflict becomes easier to manage. Ignoring conflict makes it worse; causing:
- Miscommunication
- Hidden tension
- Absenteeism
- Health issues
- High turnover
Key Takeaway:-
When employees don’t finish tasks or conflicts appear, it’s rarely because they don’t care. Most of the time, it’s because:
- They’re unclear
- They feel unheard
- They fear making mistakes
- Expectations were not communicated properly
Modern conflict management is about creating a workplace where people can speak honestly, understand each other.
References
- Conflict Management: Definition, Strategies, and Styles, Coursera, 2025.
- F. Smiley, Leadership Guide to Conflict and Conflict Management, Ohio State PressBooks (2018).
- Morton Deutsch, Peter T. Coleman & Eric C. Marcus (Eds.), The Handbook of Conflict Resolution.
- ANIRUDH SINGH, DR. SHILPA BAHL, Effect of Generational Differences in the Workplace, JOIREM.
- Mary Scannell, The Big Book of Conflict Resolution Games.
- Harvard Business School Online – Conflict Management insights.
- CIPD Report – Managing Conflict in the Workplace. (Ref 1)




