What is HR’s Strategic Role?
The strategic role of Human Resources (HR) goes beyond traditional administrative tasks like hiring, payroll, and compliance. It focuses on aligning the people strategy with the organization’s overall goals and long-term vision to drive business success.
Key Elements of HR’s Strategic Role:

- Workforce Planning & Talent Management: Ensures the right people are in the right roles at the right time. This includes:
- Succession planning
- Talent acquisition and retention
- Leadership development
- Driving Organizational Change: HR acts as a change agent by helping leaders and employees adapt to transformations like restructuring, digitalization, or mergers.
- Shaping Organizational Culture: Builds and nurtures a high-performance culture that aligns with company values and promotes employee engagement.
- Strategic Workforce Development: Identifies future skill needs and develops learning & development programs to prepare the workforce for upcoming challenges.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Uses HR analytics to provide insights on employee performance, turnover, productivity, and engagement to inform strategic decisions.
- Aligning HR Policies with Business Objectives: Ensures that HR practices (like performance management, rewards, and benefits) support the company’s goals and competitive advantage.
- Enhancing Employer Brand: Plays a role in how the company is perceived by potential and current employees, affecting its ability to attract top talent.
Example:
In a company aiming to expand into new markets, HR’s strategic role might involve:
- Identifying and developing leaders to manage international teams
- Ensuring cross-cultural training
- Adjusting HR policies to local labor laws
- Supporting a global talent acquisition strategy
HR’s Strategic Role in Organizational Culture Change
Human Resources plays a critical strategic role in driving and sustaining organizational culture change, ensuring that culture transformation aligns with business goals and is embraced throughout the organization. These courses in change management, organizational development certification can enhance your skills about the topic.
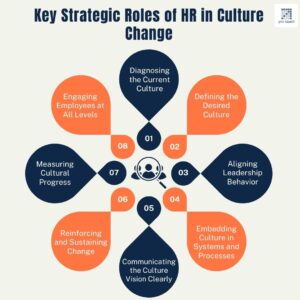
Key Strategic Roles of HR in Culture Change:
- Diagnosing the Current Culture: HR leads culture audits, employee surveys, interviews, and focus groups to assess the existing culture—identifying strengths, gaps, and areas needing change.
- Defining the Desired Culture: HR collaborates with leadership to define a clear vision for the new culture, often linked to strategic goals like innovation, customer focus, or agility.
- Aligning Leadership Behavior: HR ensures leaders model the desired behaviors, since employees mirror what leaders do more than what they say. Leadership coaching and development are key here.
- Embedding Culture in Systems and Processes: HR aligns recruitment, performance management, promotions, recognition, and training processes with the desired cultural values. Example: If collaboration is a desired value, performance reviews must reward team outcomes, not just individual success.
- Engaging Employees at All Levels: HR facilitates workshops, communication campaigns, and change agents or champions programs to involve employees, address resistance, and build emotional buy-in.
- Communicating the Culture Vision Clearly: HR plays a central role in communicating the “why, what, and how” of the culture change—helping employees see how their work connects to the bigger purpose.
- Reinforcing and Sustaining Change: Through consistent feedback, recognition programs, and cultural KPIs, HR ensures the new culture becomes embedded and not just a one-time initiative.
- Measuring Cultural Progress: HR uses surveys, behavior tracking, and other metrics to track culture shifts and report progress to leadership, making adjustments when necessary.
Example in Action:
A company moving from a hierarchical to a collaborative culture might have HR:
- Redesign job roles to promote cross-functional teams
- Train leaders in servant leadership
- Modify appraisal systems to reward teamwork
- Create platforms for peer recognition and feedback
Conclusion:
HR’s strategic role is about being a proactive business partner—not just managing people, but enabling the organization to grow, adapt, and compete effectively through its people.
Another important role in organizational culture change is about orchestrating a deep transformation—from mindset to behavior—by embedding culture in every part of the employee experience. It requires vision, alignment, engagement, and continuous reinforcement to succeed.
As we all know the HR’s strategic role in organizational culture change is vital to building a workplace that aligns with the company’s vision and values. By diagnosing the current culture, defining the desired state, aligning leadership and systems, and engaging employees throughout the journey, HR acts as a key driver of meaningful and lasting transformation. A strong, strategically guided culture not only boosts performance and engagement but also gives organizations a competitive edge in a rapidly changing business environment. Enhance your skills with these courses in change management, organizational development certification.





Leave a Reply